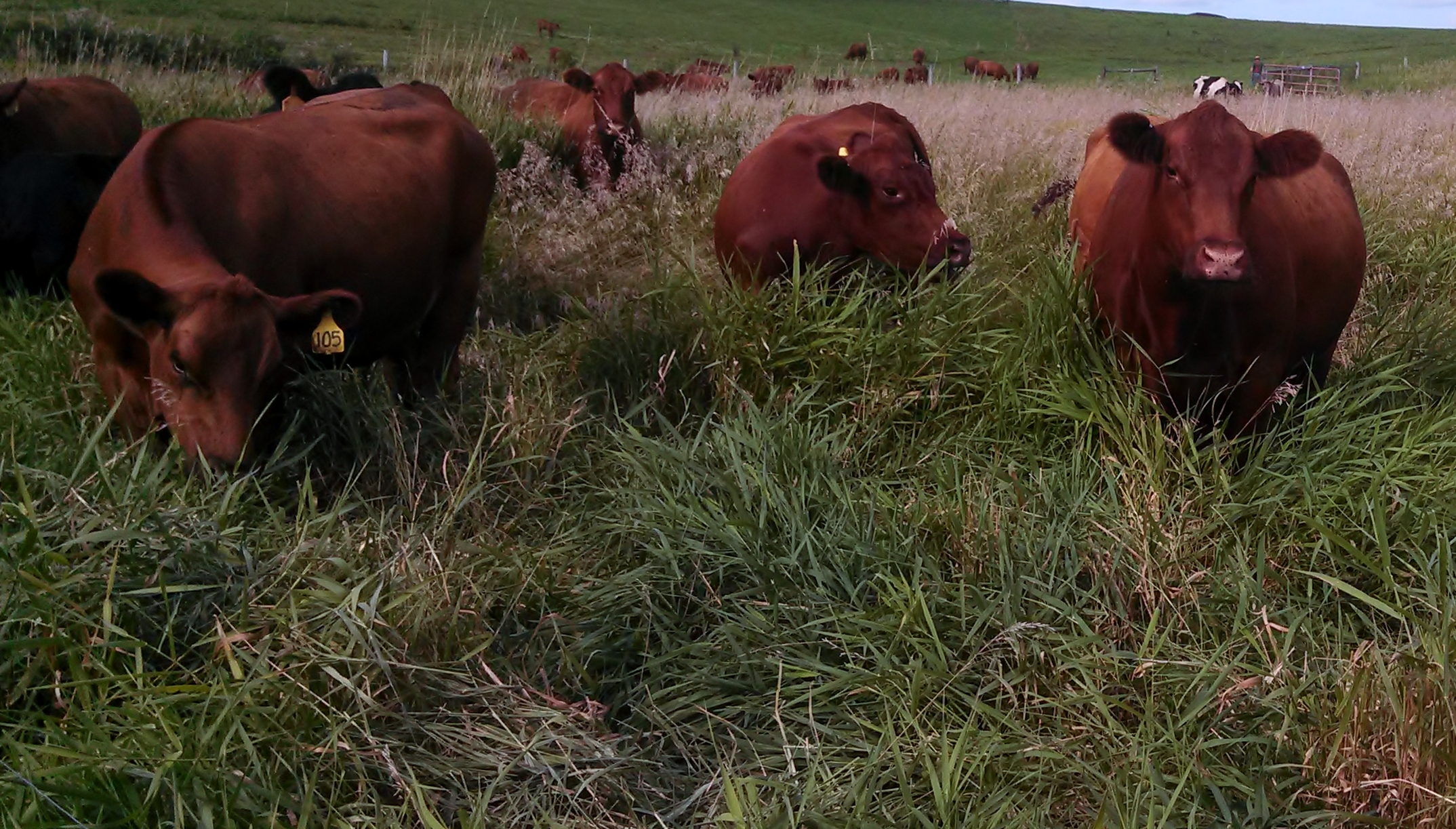
 We've heard from many people concerned over the drought in Iowa. The Drought Monitor determined that 59% of the state is in severe drought. We are concerned and are trying to prepare for the worst. We're implementing a drought plan we've had in place for a few years, just in case. Because we rotationally graze, the ground has additional recovery time between foraging. During drought conditions overgrazing certain areas by increasing the stocker rate (number of cattle in a paddock) and allowing them more time in each paddock, gives larger areas of pasture more time to recover. This allows deep rooted legumes, weeds, and less palatable plants to hold the ground, keeping the soil in place when rain returns. If the weeds or cover crop were killed off, soil erosion would be accelerated. Soil erosion would leave very poor conditions for plant recovery.
We've heard from many people concerned over the drought in Iowa. The Drought Monitor determined that 59% of the state is in severe drought. We are concerned and are trying to prepare for the worst. We're implementing a drought plan we've had in place for a few years, just in case. Because we rotationally graze, the ground has additional recovery time between foraging. During drought conditions overgrazing certain areas by increasing the stocker rate (number of cattle in a paddock) and allowing them more time in each paddock, gives larger areas of pasture more time to recover. This allows deep rooted legumes, weeds, and less palatable plants to hold the ground, keeping the soil in place when rain returns. If the weeds or cover crop were killed off, soil erosion would be accelerated. Soil erosion would leave very poor conditions for plant recovery.
As unpleasant as the subject is, culling older herd animals is necessary. A few favorite cows are going to be sold, two horses were sold, and a third is being advertised for sale. There isn't enough hay for the profitable animals so the older animals and recreational pets have to go. It's tough. These are difficult decisions but necessary to sustain the herd and the land.
The sheep who are prone to overgraze deep rooted forages while ignoring grasses have been brought closer to the barn for management. If confined to smaller areas, the sheep will eat weeds and clean up grasses and dry pasture matter. The saying, "Beggars can't be choosers", applies. Another drought management option is early weaning. The calves and lambs are offered better grazing areas and the cows and ewes reduce their required feed intake by up to 40% when not lactating.
The dairy cows and calves haven't been separated, yet. Their yield is high and milk for the pigs keeps grain costs to a minimum. Sows, boars, and feeder pigs are grazing in smaller pasture areas, keeping rooting behavior to a minimum.
Hay prices and the rising cost of grain has us looking at changing our production model. This year we'll be selling off most of the feeder pigs. Carrying them through the winter months when grain prices will be at their highest would drive prices too high. We'll hold onto our sows and boars and breed for late spring rather than late winter farrowing.
With all of these practices in place we're optimistic about the coming year. As our friend says, "Every dry day that passes gets us one day closer to rain". He's right. Eventually it will rain. That's inevitable. The question is... when. Until that day our drought plan is in full force.
This would be the time to buy larger quantities of meat. The price is only going higher, at least until the next harvest season. Planning ahead can make a big difference in your budget.
Warmest wishes and food for thought,
Glenda










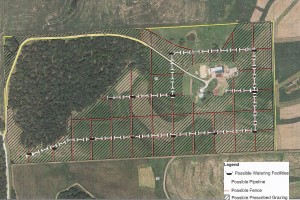




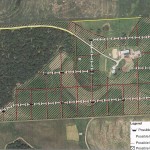
















 We've heard from many people concerned over the drought in Iowa. The
We've heard from many people concerned over the drought in Iowa. The 

